Jul. 31, 2025
Ear Pressure Relief: Home Treatment Options and Online ENT Consultations

Jump to
Book a visit
$25 typical copay
$100 without insurance
Get a legitimate doctor's note online today for work or school.
“Eustachian tube dysfunction” is a mouthful, but what it means is feeling pressure or fullness in one or both of your ears. The best method for relieving the sensation will depend on whether your ear’s tube is stuck in a closed or open position. But either way, some at-home remedies can help.
Once, after swimming in some brackish backwater on a trip, I flew home and experienced a searing pain in my left ear. An ear infection had caused my ear tube to become “blocked.” And the pressure changes from the flight had triggered the pain. I quickly found myself researching ear pressure relief.
Thankfully, with some quick remedies followed by an antibiotic from my primary care physician, I was able to relieve my ear pain. But not long after, I found myself seeing an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) physician. This time, my Eustachian tube was “stuck open,” leaving me with autophony, a condition where your own voice or breathing sounds unusually loud or echoey in your ear. I felt like I was trapped in an echoing barrel when I talked or breathed. This also resolved after some minor treatments, but it crops up again on occasion, especially when I’m running in humid weather.

Eustachian tube explanation
Turns out I have Eustachian tube dysfunction. Sometimes my eustachian tubes get stuck closed or open and I have to turn to some at-home techniques to fix the issue. If you, too, experience these ear annoyances, you might be wondering what resolves the discomfort. In this article, we explore how to get rid of ear pressure, ear pressure pain relief, what to do if your tubes are stuck open, common causes of eustachian tube dysfunction, and more.
Understanding ear pressure: common causes
You have a Eustachian tube in each ear that performs three key functions.
- Drains secretions from the middle ear
- Protects the middle ear from nasal and throat secretions
- Aids with ventilation and regulates ear pressure
That last bullet point is key to understanding why you might experience pressure in your ear.
"The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat,” says Gavin Le Nobel, MD, and ENT at Houston Methodist. “When the tube becomes blocked—often due to viral infections—it leads to a pressure imbalance behind the eardrum. This can cause symptoms like ear fullness or pressure, muffled hearing and discomfort during altitude changes or with swimming, flying or driving through mountains."
The Eustachian tubes typically remain closed. But they temporarily open to help equalize the pressure outside the ear with the pressure in the middle ear.
"The tube is supposed to open briefly when you swallow, yawn or chew, allowing air in and out of the middle ear,” Dr. Le Nobel says. “If it’s swollen or blocked, that air movement is restricted which causes pressure to build up."
The pressure results if the swelling or blockage prevents the tube from opening properly. Other times, one or both of the Eustachian tubes will open and get “stuck” in that position.
When your Eustachian tube slacks off in these ways (either failing to open or staying open), you experience eustachian tube dysfunction. The experience can be acute (temporary, lasting less than three months) or chronic (lasting more than three months).
I can attest that the situation of ear tube misbehavior can be maddening, so understanding what’s going on, your specific triggers, and the potential remedies for each type of Eustachian tube dysfunction can help.3 categories of Eustachian tube dysfunction
The type of Eustachian tube dysfunction you have will offer clues to your triggers and how to treat. So let’s get a bit technical with the tubes.
Baro-challenge induced: The door’s stuck shut
- What it is: The tube fails to open with situational changes in surrounding pressure. This creates the classic feeling of pressure in your ear.
- Causes: Often people with baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction have normal ear structure, but pressure changes can cause inflammation, leading to swelling that prevents the tube from opening to relieve pressure.
- Triggers: Scuba diving or snorkeling, landing during air travel, elevator rides, changes in altitude, and changes in atmospheric pressure (such as during a storm).
Dilatory: The inflammation blues
- What it is: Swelling blocks the tubes, preventing them from opening. This also causes a classic feeling of pressure.
- Causes: Various factors can cause inflammation of the mucus membranes of the upper respiratory tract, including nasal passages, leading to swelling.
- Triggers: Exposure to allergens, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), sinus infection, ear infection, the common cold or seasonal flu, complications from ENT surgeries, and more.
Patulous: Failure to launch—er, close
- What it is: The tube fails to close at rest. Even though the tube is open, you may still feel as if your ear is “full.” You might also experience tinnitus and mild hearing loss, and you might find yourself sniffing a lot to equalize the pressure.
- Causes: The root cause is unknown, but several factors appear to trigger it.
- Triggers: Dehydration, strenuous exercise, high heat and humidity, excessive caffeine intake, weight loss, pregnancy or perimenopause, stress or anxiety, neurological disorders, diseases affecting the immune system, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) issues, and certain medications, including hormone replacement therapy (HRT), decongestants, and antihistamines.
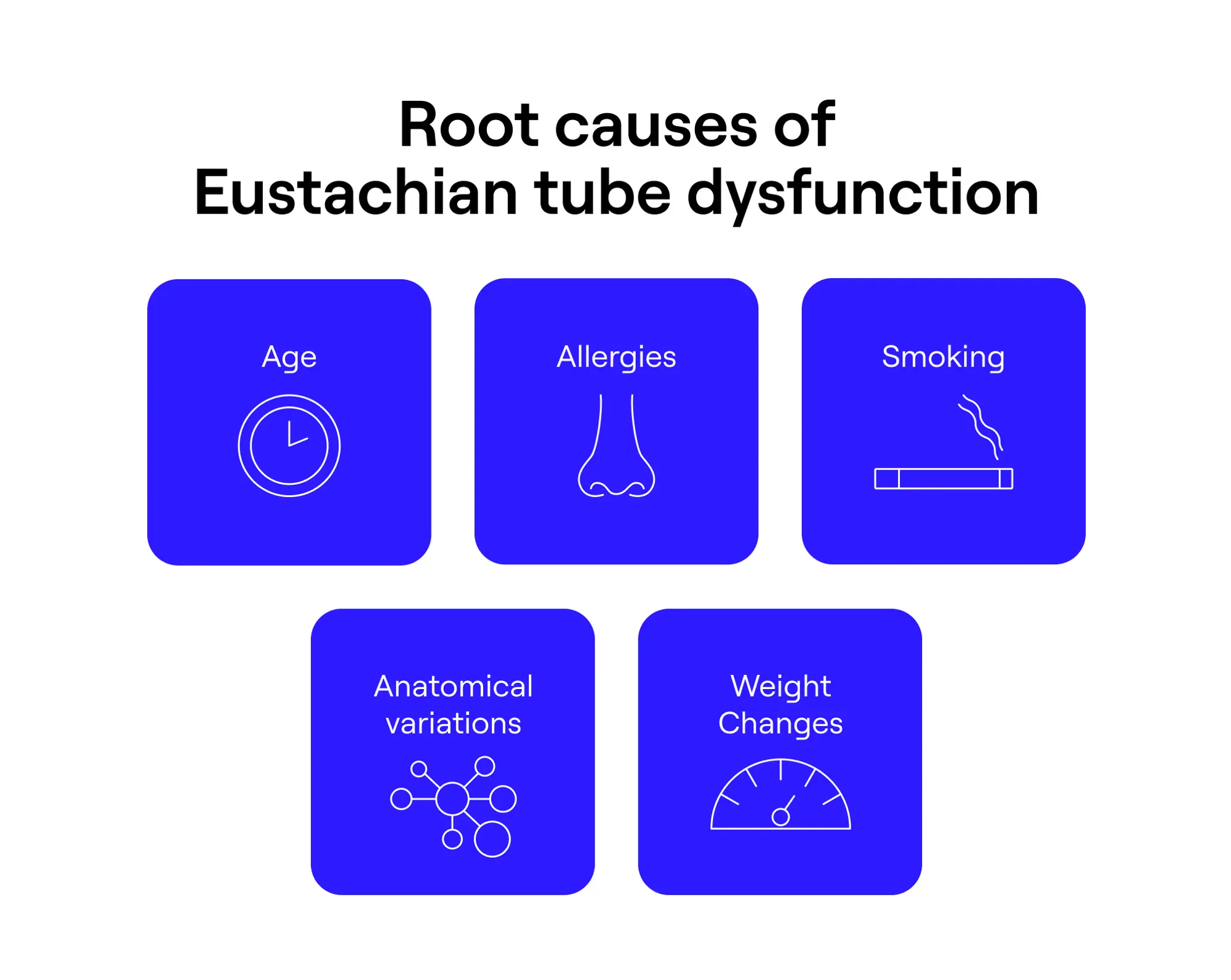
Root causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction
I’ve experienced all three types of Eustachian tube dysfunction, leading me to lament, “Why me?” The answer is complicated. Some people (raises hand) may just be more prone to the issue. For me the answer is allergies combined with an anatomical variation in my left ear.
For you, the following factors may predispose you to Eustachian tube issues.
- Age: Children have shorter Eustachian tubes, making them more susceptible to pressure changes, such as from air travel.
- Allergies: People with allergies may experience more inflammation of their upper respiratory tract, leading to swelling that causes a blockage. Plus, meds used to treat allergies can reduce inflammation so much that the tubes stay open.
- Smoking: If you’re a current or previous smoker, you may have damaged cilia. Cilia, tiny hair-like structures, are responsible for moving mucus from the ears to the throat, so when they don’t function properly, mucus can build up.
- Anatomical variations: Some people simply have narrower or wider Eustachian tubes, leading to some level of dysfunction with closing, opening, or both.
- Weight changes: Weight gain or loss can also affect ear anatomy because of increases or decreases in soft tissue around the Eustachian tubes, affecting their ability to regulate pressure.
Root causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction
Signs that ear pressure needs attention
You may be wondering when to consult a provider to bend their ear about your ear issue.
"While Eustachian tube dysfunction is usually mild and resolves on its own, you should consult a doctor if you experience ear pain with fever, persistent pressure, or hearing loss lasting more than a few days, fluid draining from the ear or dizziness or sudden changes in hearing,” says Dr. Le Nobel. “These symptoms could indicate an infection, fluid buildup or more serious issues that may require treatment."
In rare cases, tumors (cancerous or benign) can sometimes cause Eustachian tube dysfunction. So an evaluation is always a good idea if pressure does not resolve.
You should consult a provider if you experience:
- Persistent discomfort related to ear pressure
- Ear pain or pressure with fever
- Ear pain with drainage
- Hearing changes
- Tinnitus that is lasting or bothersome
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Mental health concerns, such as anxiety or depression, brought on by frustrating symptoms
- Ongoing or frequent feelings of pressure, fullness, or autophony
Effective home remedies for ear pressure relief
With a better understanding of underlying causes and factors that can trigger that feeling of a blocked or full ear or that annoying autophony, you might be wondering what helps with ear pressure quickly. Treatment for you may involve both prevention and instant relief techniques.
"There are a few techniques that may help relieve the pressure, like swallowing, yawning or chewing gum,” Dr. Le Nobel says. “These can activate the muscles that open the Eustachian tube. The Valsalva maneuver, gently blowing with your nose pinched and mouth closed, and the Toynbee maneuver, pinching your nose and swallowing, can also help.” (Instructions for these maneuvers are in the next section.)

Techniques to relieve ear pressure
Baro-challenge induced
- Prevention: “Before flying, using a nasal decongestant spray about 30 minutes before takeoff and landing can help reduce discomfort,” says Pallabi Sanyal-Dey, MD, medical director of General Medicine. “Using filtered earplugs can also ease pressure changes. Staying well hydrated and avoiding alcohol may further support eustachian tube function.”
- Relief: Try the Valsalva maneuver, Toynbee maneuver, or Eustachian tube massage (see below for instructions for both). You can also sip water or another beverage to initiate swallowing, or open and close your jaw, chew gum, or yawn. Specialized ear plugs, such as Ear Planes, help regulate ear flow into the ear. These can work well if you’re prone to pressure when you fly or change elevation.
Dilatory
- Prevention: Make sure your allergies or GERD are well controlled by taking all prescribed medications and treatments as directed. If you have a sinus infection, cold, or other upper respiratory infection, you may wish to treat your symptoms with an over-the-counter decongestant, which can help reduce mucus membrane inflammation and ease Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Relief: Try the Valsalva maneuver, Toynbee maneuver, or Eustachian tube massage (see below for instructions for both). You can also sip water or another beverage to initiate swallowing, or open and close your jaw, chew gum, or yawn.
Patulous
- Prevention: Stay hydrated and limit caffeine.
- Relief: A quick sniff or two can create a vacuum that closes the Eustachian tube. But use this method sparingly, as it can cause a buildup of middle ear pressure that affects the ear drum. Also, try lying down temporarily. This increases pressure, helping to close the tube. (This type of Eustachian tube dysfunction plagues me the most. My method is to use the sniff technique if I can’t lie down, such as when I’m running. But if I can lie down, I do that instead, as it is more effective.)
Instant relief techniques for ear pressure
The above section mentions three techniques for relieving ear pressure if you have baro-challenge-induced or dilatory Eustachian tube dysfunction. Here are the instructions for each.
What is the Valsalva maneuver?
One of the most instant-relief techniques for ear pressure is to do the Valsalva maneuver.
- Sit or lie comfortably.
- Take a slow deep breath.
- Close your mouth and pinch your nostrils shut.
- Gently exhale against your closed airways.
- Hold for about 15 seconds.
- Rest a few minutes before repeating if necessary.
“Just be cautious not to blow too hard,” Dr. Le Nobel says, “especially if you’re congested or recovering from a cold, as this can sometimes worsen symptoms."
While these maneuvers can help equalize pressure, improper or forceful use may worsen symptoms or cause harm, particularly in people with underlying ear or neurological conditions. A medical evaluation can help determine the safest and most effective approach for your symptoms. You should not do the Valsalva maneuver if you have any of the following conditions unless your doctor has recommended it:
- Retinopathy
- Intraocular lens implants
- A heart condition (arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, congenital heart disease)
- High blood pressure
- Ear trauma
- Ear infection
What is the Toynbee maneuver?
The Toynbee maneuver is like the Valsalva maneuver, but it involves less force, reducing the risk for potential issues.
Toynbee maneuver:
- Sit or lie comfortably.
- Take a slow deep breath.
- Pinch your nostrils shut.
- Swallow.
- Rest a few minutes before repeating if necessary.
What is Eustachian tube massage?
Applying gentle pressure to your neck can also help relieve this type of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Find the groove between your jawbone and the bony protrusion behind your earlobe.
- Gently trace the groove down your neck to your collarbone.
- Repeat several times.
What not to do for a sore ear
We’ve shared what to do, but knowing what not to do can be just as important—so as not to harm your ear.
“Avoid inserting any object (including Q-tips!) into your ear,” says Poushali Bhattacharjee, MD, a physician with General Medicine. “Finally, if you have a cold or nasal congestion, forcing air into blocked tubes can actually make things worse (e.g., push bacteria into the middle ear),” Dr. Bhattacharjee adds.
Believe me, the idea of messing with your ear is tempting when you have pressure buildup or have that feeling of wind or fullness in there. But you don’t want to risk any damage.
You may be wondering if heat, over-the-counter ear drops, or essential oils or olive oil might work, as these remedies sometimes show up online. Using a warm compress may offer temporary relief from ear infection pain, but it isn’t a remedy for eliminating the infection, which is necessary to reduce pressure. Over-the-counter drops lack efficacy. And essential oils aren’t safe or effective. Olive oil, however, is a remedy to soften earwax buildup, which may be blocking the ear canal, causing a sensation of fullness. While olive oil can help soften earwax, it does not treat Eustachian tube dysfunction directly. Only use it if your provider confirms that earwax is the issue.
Other old wives’ tales, such as cold leg compresses or onion wraps “to draw out toxins” have no evidence to back them up.
Where to get care
If you need medical care for chronic or frequent acute Eustachian tube dysfunction, you can reach out to your primary care provider. If your symptoms persist beyond three months, recur frequently, or significantly affect daily life, consider asking your PCP for an ENT referral to an expert who specializes in these exact issues. ENTs offer advanced testing and treatment options—such as hearing evaluations, imaging, and procedures like Eustachian tube balloon dilation—for more complex or chronic cases.
You can opt for a telehealth appointment if that’s more convenient for you. “ENT-oriented telehealth visits offer quick, convenient access to care, especially for patients in remote areas or those who prefer to avoid in-person visits,” Dr. Sanyal-Dey says.
“They are effective for evaluating common issues like sinus congestion, ear pain, and allergies, and can help determine whether in-person care is needed,” she adds. “In some cases, patients can share ear images using digital tools to support remote diagnosis.”
A provider will review your symptoms, walk you through self-treatment techniques, prescribe any needed medications, and provide referrals when necessary.
Key takeaways
- Eustachian tube dysfunction is a common cause of ear pain and pressure.
- It occurs when your tubes fail to open when equalizing pressure or fail to return to their usual closed position.
- Some at-home remedies can help, but if your symptoms reoccur or don’t resolve, talk to a provider.
- You can book a telehealth appointment for an assessment and to learn relief techniques. This can also determine if you need an in-person evaluation.
General Medicine follows a strict editorial process, including using real experts to write our articles, vetted primary sources, fact-checking, a secondary medical review, and updates as necessary. This article was medically reviewed and fact checked by Pallabi Sanyal-Dey, MD, and Poushali Bhattacharjee, MD.
FAQ
How to unblock pressure in the ear?
If you are experiencing pressure in your ear, you may have a blocked Eustachian tube. To relieve the pressure, you can sip water or another beverage to initiate swallowing, open and close your jaw, chew gum, or yawn. Or try the Valsalva maneuver: Sit or lie comfortably, take a slow deep breath, close your mouth and pinch your nostrils shut, gently exhale against your closed airways, hold for about 15 seconds, and rest a few minutes before repeating if necessary. A gentler alternative to the Valsalva maneuver is the Toynbee maneuver. Instead of blowing, you swallow.
Is there a pressure point to unclog ears?
Gentle neck pressure may help unclog your ears. Apply gentle pressure to your neck by finding the groove between your jaw bone and the bony protrusion behind your earlobe. Gently trace the groove down your neck to your collarbone.
Why do I feel pressure in my ear?
Your ears have Eustachian tubes. The tubes remain closed most of the time, but they open to equalize inner ear pressure with environmental pressure. Sometimes the tubes fail to open or fail to close after opening. When they fail to open, you may experience pain and pressure. When they fail to close, you may experience the sensation of fullness or air in your ear and autophony, hearing your own voice or breath or as if you’re talking with an echo.
How to open a Eustachian tube?
If you are experiencing pressure in your ear, you may have a blocked Eustachian tube. To relieve the pressure, you can sip water or another beverage to initiate swallowing, open and close your jaw, chew gum, or yawn. Or try the Valsalva maneuver: Sit or lie comfortably, take a slow deep breath, close your mouth and pinch your nostrils shut, gently exhale against your closed airways, hold for about 15 seconds, and rest a few minutes before repeating if necessary. A gentler alternative to the Valsalva maneuver is the Toynbee maneuver. Instead of blowing, you swallow.
How do I get immediate relief from an earache?
If you have an earache, the best way to find relief will depend on the cause. If your ear pain is from pressure, then relieving the pressure by swallowing or doing the Valsalva maneuver (described in this article) may help, but it warrants caution. If you have an ear infection or fever, you will need an evaluation from a medical professional.
Our editorial standards
At General Medicine, we cut through the clutter to make health care clearer, faster, and easier to navigate. Every article is grounded in evidence-based research and peer-reviewed journals, reviewed by medical professionals, and written in accessible language that helps you make health decisions with confidence. We’re committed to ensuring the quality and trustworthiness of our content and editorial process by providing information that is up-to-date, accurate, and actually useful. For more details on our editorial process, see here.



